Low battery
Battery level is below 20%. Connect charger soon.
1996 Nissan Pickup Fuse Box Diagram – Full Layout Explained
The 1996 Nissan Pickup, a reliable workhorse of its era, continues to serve owners well. However, electrical issues are a common concern in older vehicles. Understanding the location and function of your 1996 Nissan Pickup’s fuses is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining its electrical system. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed breakdown of the fuse box layout, helping you quickly identify and replace blown fuses, keeping your pickup running smoothly.
Understanding Your 1996 Nissan Pickup’s Fuse Boxes
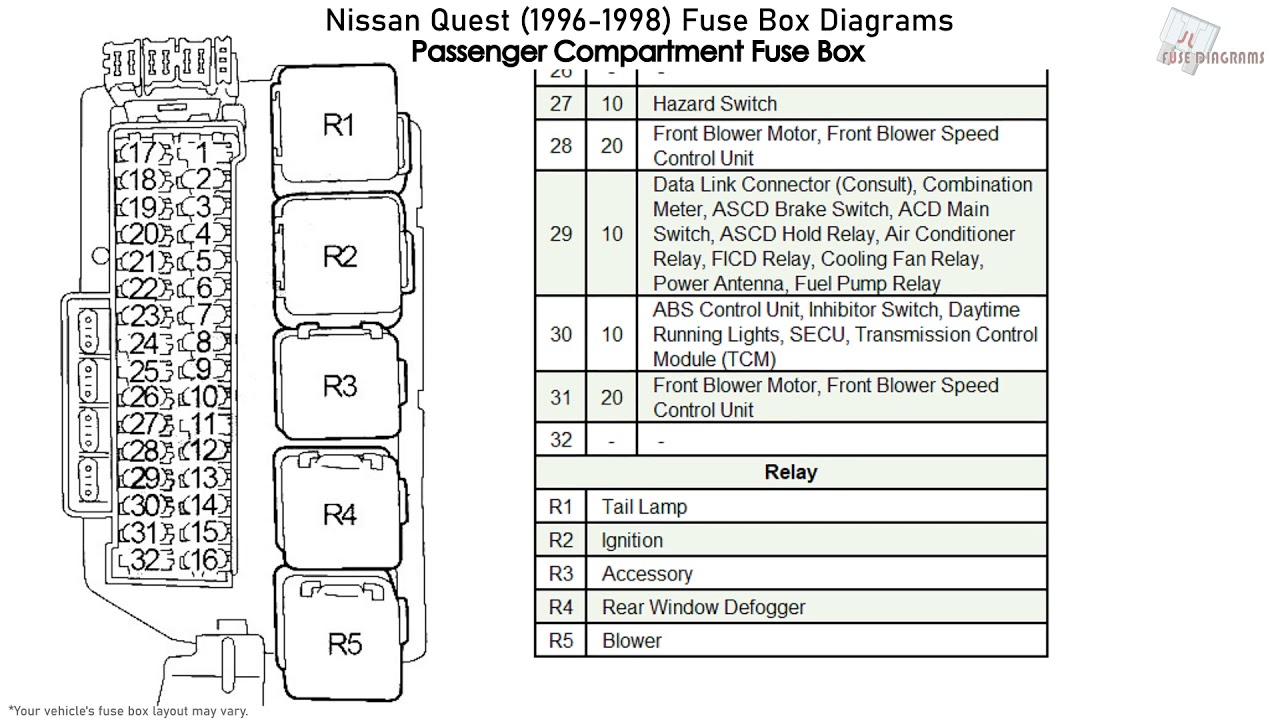
The 1996 Nissan Pickup typically features two fuse boxes:
- Main Fuse Box (Engine Compartment): This box houses the primary fuses and relays that protect crucial engine components, lighting systems, and other essential circuits.
- Secondary Fuse Box (Interior - Dash or Kick Panel): This box typically manages fuses for interior accessories like the radio, power windows, and interior lights.
Before you begin, always disconnect the negative terminal of your battery to prevent accidental shorts and potential electrical damage.
Main Fuse Box (Engine Compartment) Diagram & Functionality
The main fuse box is usually located under the hood, often near the battery or on the driver’s side. The exact location may vary slightly, so consult your owner’s manual for precise placement. The lid of the fuse box often contains a diagram, but it can be difficult to read or may have faded over time. Here’s a breakdown of common fuse functions within the main fuse box:
- Fuses: Protects high-amperage circuits from overcurrent.
- Relays: Act as electronic switches, controlling high-power components with a smaller electrical signal.
Common Fuse Functions (Example - Consult Your Owner’s Manual for Exact Configuration):
- Main Fuse(s): Protects the entire electrical system. (High Amperage, often 80-100A or higher).
- Headlights: Controls the low and high beam headlights.
- Horn: Powers the vehicle’s horn.
- Ignition: Supplies power to the ignition system.
- Starter: Powers the starter motor.
- Fuel Pump: Provides power to the fuel pump.
- ABS (if equipped): Controls the Anti-lock Braking System.
- Cooling Fan: Powers the engine cooling fan.
- Wiper Motor: Controls the windshield wipers.
- Charging System: Protects the charging circuit.
How to Identify a Blown Fuse in the Engine Compartment:
- Locate the Fuse Box: Identify the fuse box under the hood.
- Consult the Diagram (or Owner’s Manual): Use the diagram on the fuse box lid or your owner’s manual to identify the fuse related to the malfunctioning component.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine each fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken filament within the clear plastic housing.
- Use a Fuse Tester (Recommended): A fuse tester provides a quick and accurate method for checking a fuse’s functionality.
Secondary Fuse Box (Interior) Diagram & Functionality
The secondary fuse box, located inside the vehicle, is typically found on the driver’s side dashboard or kick panel. It’s often behind a removable panel.
Common Fuse Functions (Example - Consult Your Owner’s Manual for Exact Configuration):
- Radio: Powers the audio system.
- Cigarette Lighter/Power Outlet: Provides power for accessories.
- Interior Lights: Controls the dome lights and other interior illumination.
- Power Windows (if equipped): Operates the power windows.
- Power Door Locks (if equipped): Controls the power door locks.
- Tail Lights: Controls the tail lights and brake lights.
- Turn Signals: Controls the turn signals and hazard lights.
- Heater/AC Blower Motor: Powers the climate control system.
How to Identify a Blown Fuse in the Interior:
- Locate the Fuse Box: Find the interior fuse box, usually on the driver’s side.
- Consult the Diagram (or Owner’s Manual): Use the diagram on the fuse box lid or your owner’s manual to identify the fuse related to the malfunctioning component.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine each fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken filament within the clear plastic housing.
- Use a Fuse Tester (Recommended): A fuse tester provides a quick and accurate method for checking a fuse’s functionality.
Replacing a Blown Fuse
- Safety First: Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Locate the Correct Fuse: Identify the blown fuse using the diagram.
- Remove the Blown Fuse: Use a fuse puller (often included in the fuse box lid) or needle-nose pliers to carefully remove the blown fuse.
- Install the New Fuse: Insert a new fuse with the same amperage rating into the empty slot. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified, as this can damage your vehicle’s electrical system.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Test the Component: Test the component that was previously not working. If the fuse blows again, there may be a short circuit or other electrical problem that requires professional diagnosis.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual is your primary resource for fuse box diagrams and fuse functions.
- Carry Spare Fuses: Keep a supply of spare fuses in your vehicle.
- Check for Shorts: If a fuse blows repeatedly, there may be a short circuit. Inspect the wiring for damage or exposed wires.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are not comfortable working with electrical systems, consult a qualified mechanic.
Conclusion
Understanding the fuse box layout of your 1996 Nissan Pickup is essential for maintaining its electrical system. By utilizing this guide and consulting your owner’s manual, you can easily locate, identify, and replace blown fuses, keeping your pickup running smoothly and safely. Remember to always prioritize safety and seek professional help if you encounter complex electrical issues.
FAQs
1. Where can I find the fuse box diagram for my 1996 Nissan Pickup?
The fuse box diagram is usually located on the inside of the fuse box lid. If the diagram is missing or illegible, consult your owner’s manual. You can also often find diagrams online.
2. What happens if I use a fuse with a higher amperage rating than the original?
Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can damage your vehicle’s electrical system. The fuse is designed to protect the circuit. A higher-rated fuse may not blow in time to protect components from overcurrent, potentially leading to damage or even fire.
3. My fuse keeps blowing. What should I do?
If a fuse keeps blowing, there is likely a short circuit or another electrical problem. Inspect the wiring for damage or exposed wires. It’s best to consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the underlying issue.
4. Can I use a fuse puller to remove the fuses?
Yes, a fuse puller is recommended. They are often included in the fuse box lid. If you don’t have a fuse puller, you can use needle-nose pliers, but be careful not to damage the fuse box or surrounding components.
5. Are there any differences in fuse box layout for different trim levels of the 1996 Nissan Pickup?
While the core functions are generally the same, there might be minor variations in the fuse box layout based on the trim level or optional equipment installed on your specific 1996 Nissan Pickup. Always refer to your owner’s manual for the most accurate diagram for your vehicle.