Low battery
Battery level is below 20%. Connect charger soon.
Layout 2012 VW Passat Fuse Box Diagram: The Map Every Owner Needs for Quick Fixes
Owning a 2012 Volkswagen Passat is a rewarding experience, offering a blend of comfort, performance, and German engineering. However, like any vehicle, electrical issues can arise. When a light flickers, the radio goes silent, or the power windows cease to function, the culprit is often a blown fuse. Knowing the layout of your 2012 VW Passat fuse box diagram is crucial for quick troubleshooting and getting you back on the road swiftly. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, empowering you to confidently identify and replace fuses, saving you time and potentially costly trips to the mechanic.
Understanding the Importance of a Fuse Box Diagram
A fuse box diagram, essentially a map of your vehicle’s electrical system, is an invaluable tool. It illustrates the location and function of each fuse, allowing you to:
- Quickly identify the correct fuse: Instead of guessing, you can pinpoint the fuse responsible for a specific component.
- Prevent further damage: Replacing a blown fuse promptly prevents electrical surges from damaging other sensitive components.
- Save money: Troubleshooting and fixing minor electrical issues yourself can save you from expensive repair bills.
- Increase your understanding of your vehicle: Familiarizing yourself with the fuse box layout empowers you to understand your Passat’s electrical systems better.
Locating the Fuse Boxes in Your 2012 VW Passat
Your 2012 VW Passat typically has multiple fuse boxes strategically placed throughout the vehicle. Knowing where to find them is the first step in your troubleshooting process:
- Main Fuse Box (Interior): Located on the driver’s side dashboard, often behind a panel near the steering wheel or on the left side of the dashboard. You might need a small tool (usually included in your Passat’s toolkit) to pry open the panel.
- Secondary Fuse Box (Engine Compartment): Found in the engine bay, typically near the battery. It’s usually housed in a black plastic box with a hinged lid. This box contains fuses for essential engine components and other high-power circuits.
Important Safety Note: Before working with any electrical components, always disconnect the negative terminal of your car’s battery to prevent accidental shorts and injuries.
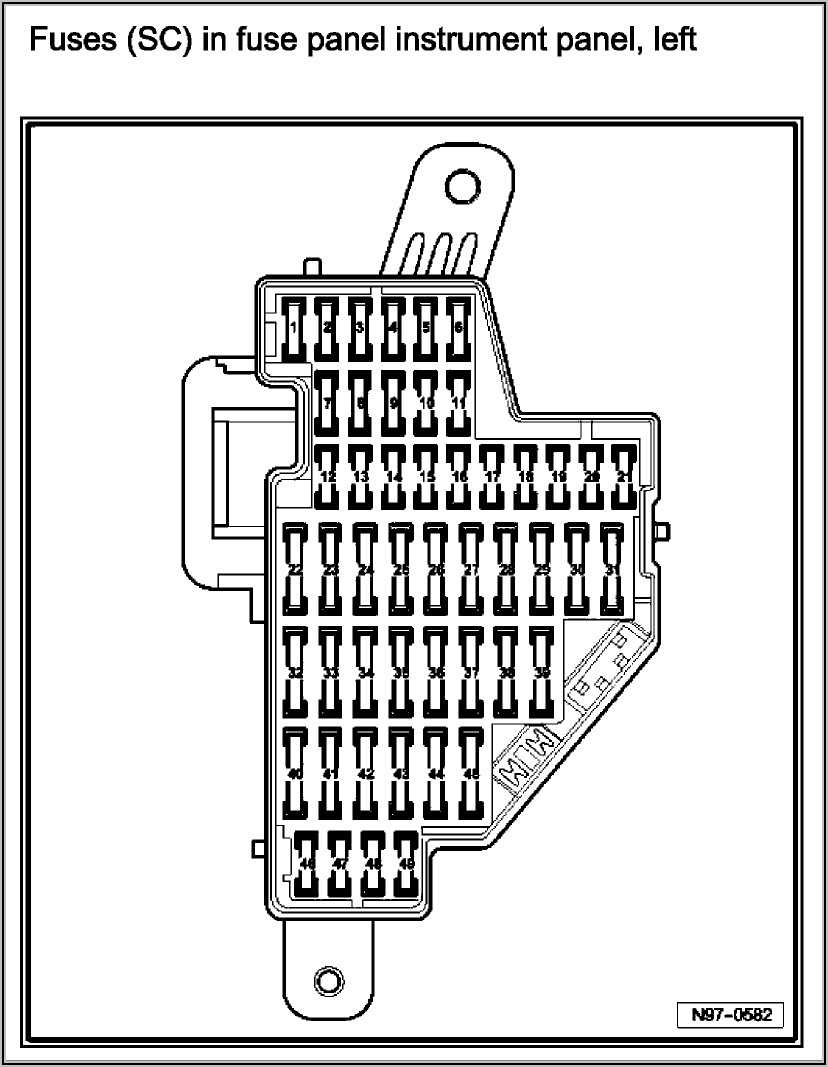
Deciphering the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram, usually found on the inside of the fuse box cover or in your owner’s manual, is your key to understanding the electrical layout. Here’s how to interpret it:
- Symbols: The diagram uses symbols to represent the various electrical components protected by each fuse (e.g., headlights, radio, power windows, etc.).
- Fuse Amperage: The diagram indicates the amperage rating of each fuse (e.g., 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, etc.). This number is crucial; always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage.
- Fuse Position: The diagram shows the exact location of each fuse within the fuse box.
- Color-Coding (Helpful Tip): Fuses are often color-coded to indicate their amperage rating, making it easier to identify the correct replacement fuse. For example, a 10A fuse is typically red, while a 20A fuse is usually yellow.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues
Armed with the fuse box diagram, you can tackle common electrical problems:
- Headlights not working: Check the fuses for the headlights (often a 10A or 15A fuse, depending on the specific lights).
- Radio not turning on: Examine the fuse for the radio (typically a 10A or 15A fuse).
- Power windows not functioning: Inspect the power window fuse (usually a 20A or 30A fuse).
- Cigarette lighter/power outlet not working: Locate the fuse for the cigarette lighter/power outlet (often a 15A or 20A fuse).
- Dashboard lights out: Check the fuses related to dashboard illumination.
Steps to Replacing a Blown Fuse:
- Locate the correct fuse: Consult the fuse box diagram to identify the fuse responsible for the malfunctioning component.
- Disconnect the battery: For safety, disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Remove the fuse: Use the fuse puller tool (usually included in your Passat’s toolkit) or small pliers to carefully remove the blown fuse.
- Inspect the fuse: Look for a broken filament inside the fuse. If the filament is broken, the fuse is blown.
- Install a new fuse: Insert a new fuse of the same amperage rating into the correct position.
- Reconnect the battery: Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Test the component: Turn on the component to see if it’s functioning correctly.
Beyond the Basics: Additional Considerations
- Owner’s Manual: Your owner’s manual is your best resource. It provides detailed diagrams, fuse descriptions, and safety instructions specific to your 2012 VW Passat model.
- Spare Fuses: Keep a supply of spare fuses in your car’s glove compartment.
- Professional Assistance: If you’re unsure about any aspect of the electrical system or cannot locate the source of the problem, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Conclusion
Understanding the 2012 VW Passat fuse box diagram empowers you to maintain your vehicle’s electrical systems effectively. By familiarizing yourself with the layout, symbols, and fuse locations, you can confidently troubleshoot and resolve minor electrical issues, saving time and money. Remember to consult your owner’s manual for specific diagrams and safety precautions, and don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance for more complex problems. By taking proactive steps, you can ensure your 2012 VW Passat continues to provide a reliable and enjoyable driving experience for years to come.
FAQs
1. Where can I find the fuse box diagram for my 2012 VW Passat?
The fuse box diagram is typically located on the inside of the fuse box cover and in your owner’s manual.
2. What should I do if I can’t find the specific fuse for a component?
Carefully examine the diagram and identify the fuse that corresponds to the component you’re troubleshooting. If unsure, consult your owner’s manual or a qualified mechanic.
3. Can I use a fuse with a higher amperage rating than the original?
No, never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating. This can overload the circuit and potentially damage components or cause a fire.
4. What should I do if the new fuse blows immediately after replacing it?
This indicates a more significant electrical problem, such as a short circuit. Do not continue replacing fuses. Seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the issue.
5. Is it safe to work on the fuse box?
Yes, it’s generally safe, provided you disconnect the negative battery terminal before working with any electrical components. Always exercise caution and consult your owner’s manual for safety instructions.